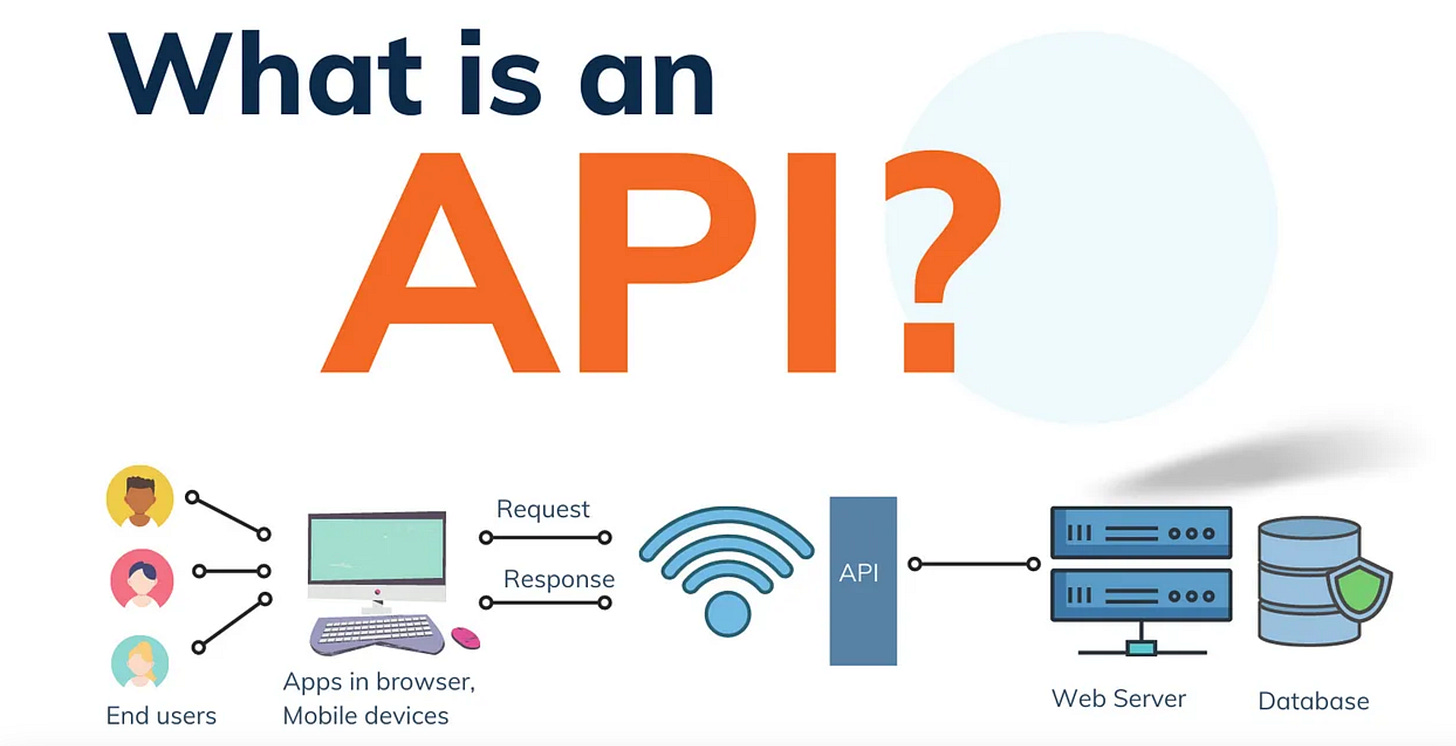
How to learn API?
As software engineers, working with APIs is part of our daily routine—whether we're building them or integrating with them. Designing REST APIs that are not only clear and easy to use but also robust.
API Roadmap
APIs are fundamental to modern software development and should be one of the first concepts software engineers master. Before diving into advanced topics like distributed systems or cloud computing, it's important to build a solid understanding of APIs. APIs serve as the foundation for how software systems interact, and learning them will also deepen your knowledge of programming languages and frameworks.
Whether you're just starting out or an experienced developer aiming to enhance your API skills, this learning roadmap will guide you through the essential concepts and technologies.
1. Introduction to APIs
Before tackling API development, it's important to grasp the basics. This includes understanding the protocols and principles that underpin APIs and their role in modern software systems.
Key Concepts: Learn foundational topics such as the HTTP protocol, DNS, URLs, and more.
What is an API?: APIs are sets of protocols, routines, and tools that enable interaction between software components. They define how different parts of a system communicate.
Types of APIs:
🌐 Public APIs: Accessible to external developers (e.g., Twitter API).
🔒 Private APIs: Used internally within an organization.
🔑 Partner APIs: Shared with selected business partners.
🧩 Composite APIs: Combine data and services from multiple APIs.
2. API Architectures
Understanding various API architectural styles is critical, as each serves different use cases with unique strengths and trade-offs. These architectures determine how your API interacts with clients and integrates with other systems.
REST (Representational State Transfer): The most widely used architectural style for web APIs, emphasizing stateless communication and resources.
GraphQL: A flexible query language for APIs, allowing clients to request precisely the data they need.
SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol): A protocol designed for exchanging structured information in web services.
gRPC: A high-performance, open-source framework created by Google for efficient communication.
WebSockets: Enables real-time, full-duplex communication between clients and servers.
Webhooks: A mechanism for real-time notifications and event-driven programming.
3. API Security
API security is a cornerstone of reliable development, ensuring that APIs are protected from un-authorized access and potential vulnerabilities while safeguarding data during transmission. Below are key components and practices to fortify API security:
Authentication: Methods include Basic Authentication, OAuth 2.0, and JSON Web Tokens (JWT).
Authorization: Implement access control to ensure only authorized users can access specific resources.
Rate Limiting: Restrict the number of API calls a client can make to prevent abuse.
Encryption: Use HTTPS to secure data in transit and protect it from interception.
Best Practices: Follow OWASP's top 10 security risks for APIs to mitigate vulnerabilities.
4. API Design Best Practices
Crafting well-designed APIs ensures they are intuitive, efficient, and easy to maintain. Following established best practices makes APIs user-friendly and scalable:
RESTful Conventions: Use HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) correctly and follow clear resource naming conventions.
Versioning: Implement versioning to handle changes gracefully:
URI versioning (e.g.,
/v1/users)Query parameter versioning (e.g.,
/users?version=1)Header versioning (e.g.,
Accept: application/vnd.company.v1+json).
Pagination: Efficiently manage large datasets to enhance performance and usability.
Error Handling: Provide meaningful HTTP status codes and detailed error messages:
Reference the latest standard, RFC 9457, for problem details in HTTP APIs (replacing RFC 7807).
5. API Documentation
APIs are only as effective as their documentation. Comprehensive, clear, and user-friendly documentation ensures that developers can easily integrate and use your API. Popular tools and practices include:
Swagger/OpenAPI Specification: Standardizes RESTful API descriptions.
Postman: A widely-used tool for API documentation and testing.
ReDoc: Generates visually appealing API documentation.
DapperDox: Open-source and rich in rendering OpenAPI specifications.
Slate: A developer favorite, with over 15,000 forks on GitHub.
ReadMe: Transforms static API docs into interactive, real-time developer hubs.
6. API Testing
Thorough testing ensures APIs perform reliably and meet functional and non-functional requirements. Various tools and approaches are available for effective API validation:
Postman: Simplifies the creation and execution of API tests.
SoapUI: Supports testing for both SOAP and REST APIs.
JMeter: Focuses on performance and load testing.
API Mocking: Use tools like Mockoon or Postman mock servers to simulate API responses.
Pact: Enables contract testing, ensuring APIs adhere to specified integration agreements.
Insomnia: A cross-platform tool for debugging and testing REST, GraphQL, and gRPC APIs.
Rest-Assured: A Java library for writing REST API tests in an expressive syntax.
Katalon Studio: Comprehensive automation for web, mobile, and API testing.
Newman: A CLI tool for running Postman collections, perfect for CI/CD pipelines.
This structured roadmap will help you master APIs, from securing them to designing, documenting, and testing them effectively.